Selected nano-catalysis projects
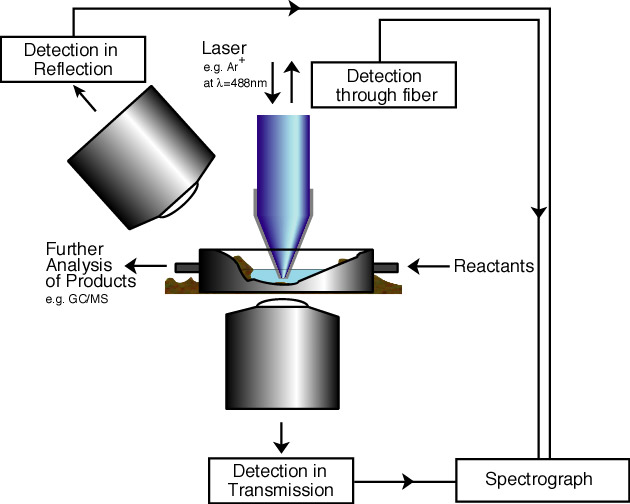 |
HistoryThe near-field spectroscopic investigation of single catalytic sites started using so-called aperture based near-field probes. A Pd catalyzed hydrogenation reaction was investigated using a silver substrate as a Raman enhancer. Strong indications of a the hydrogenation product were detected, however, the signal-to-noise ratio of aperture based methods presents a major challenge and prevented in situ high resolution invesigations.
ReferencesC. Fokas, V. Deckert, Towards in situ Raman Microscopy of Single Catalytic Sites. Appl. Spectrosc, 2002, 56, 2, 192. |
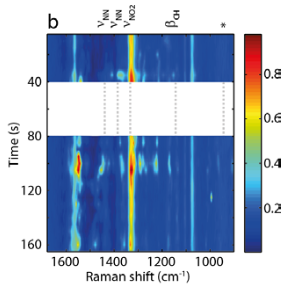 |
Direct investigation of a plasmon catalyzed reactionTERS has been applied to the investigation of plasmon catalysed reactions, namely azo coupling reactions. A dual-wavelength approach allows to use the probe as a catalyst and a plasmonic probe at the same time and such investigate reactivities with nanometer lateral resolution.
ReferencesE. M. van Schrojenstein Lantman, T. Deckert-Gaudig, A. J. G. Mank, V. Deckert,B. M. Weckhuysen Catalytic processes monitored at the nanoscale with tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat Nano, 2012, 7, 9, 583. |
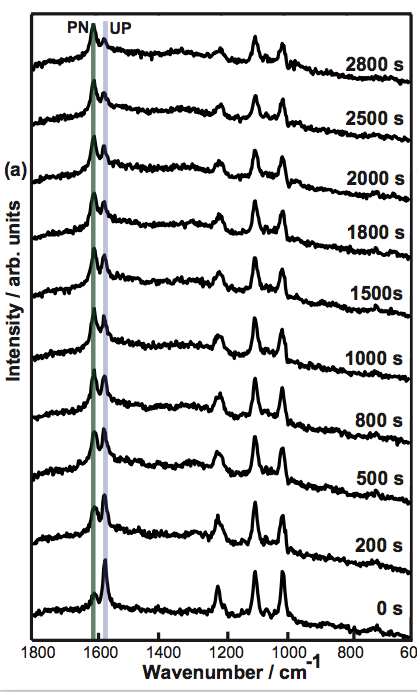 |
Plasmon mediated protonationIn special cases a plasmonic probe can induce protonation reactions. A clear distinction between atmospheric and temperature influences could be determined.
ReferencesP. Singh, V. Deckert, Local protonation control using plasmonic activation. Chem. Commun, 2014, 50, 76, 11204. |